
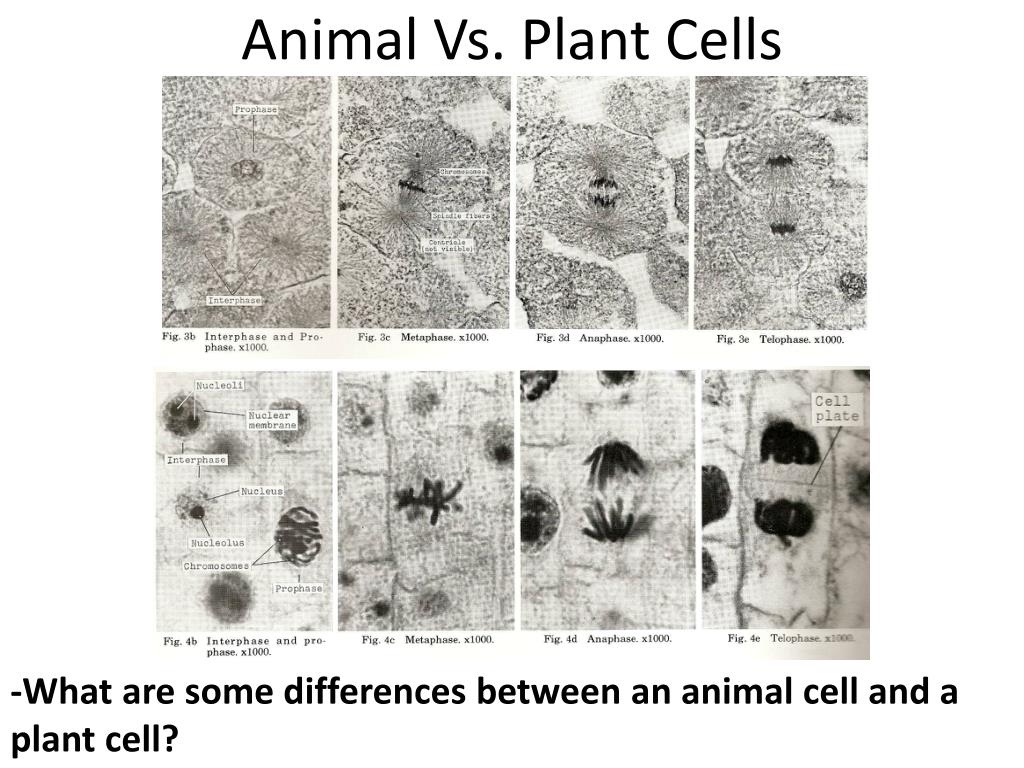
Nevertheless a number of mitotic stages can be defined: prophase (B and 2), metaphase (C and 3), anaphase (mid 4 and late D and 5), telophase (E) and cytokinesis (F and 6). The cell cycle, which includes interphase (A and 1) and mitosis, is a continuous process. Zoom in with "Shift", Zoom out with "Control", Navigate with the arrows or with a mouse drag Sometimes remants of the spindle (phragmoplast) are involved in the attachment of this new wall. In plants, this process is characterized by the formation and growth of a cell plate (example in Solanum sp.) that expands from the space between the two daughter nuclei towards the cell periphery.

In animal cells the separation of the new cells involves a cleavage furrow that pinches the cell membrane. During cytokinesis (example in Bellevalia) that follows up the actual mitosis, the cytoplasm of the daughter cells is divided by a cell membrane (and in plants also a cell wall) in two single compartments. Cytokinesis (kytos = hollow vessel = cell, and kinesis = movement): the two daughter cells become independent.The spindle disappears, the chromosomes despiralize, a new nuclear envelop is formed and the new nucleoli are visible (view of early telophase and telophase in Bellevalia) This is the conclusion of nuclear division. Telophase (telos = end): the final phase.(view of early anaphase and mid anaphase in Bellevalia) Each single chromatid can be regarded as the new chromosome from now on.
The two chromatids of each chromosome are pulled apart by the microtubules attached to the kinetochore (= a specialized area of the centromere) in the direction of the opposite poles.

Metaphase (meta = mid): the middle phase.Photographs of early, mid and late prophase stage. All chromosomes become visible and consist now of two chromatids that are joined together at the centromere. The centrosomes (consisting each of a pair of centrioles - only in animal cells) that have been duplicated during the G2-phase separate now. The chromosomes begin to spiralize and the nuclear membrane and nuclear bodies (nucleoli = place in the nucleus active in the synthesis of ribosomes) disappear. Prophase (pro = before): the preparative phase.take up nutrients, grow, read DNA and produce proteins, and prepare themselves for the mitosis, in particular by replicating their DNA. Interphase is considered as the phase during which cells conduct their "normal" cellular functions, i.e. Interphase (inter = in between): the interphase is the longste lasting stage of the cell cycle.Schematically: for diploid mothercells (for example cells of a leaf) Condensed single chromosomes can be well visualized under a light microscope. Being compact the chromosomes can be more easily separated over the daughter nuclei than if they would be unfolded. At the beginning of mitosis the nuclear envelop disappears and the chromosomes condense strongly by folding in a spiral-like way around protein molecules. The DNA is already duplicated and controled by then. The mitosis follows up the G2-phase of the interphase in the cell cycle. After mitosis and cytokinesis the daughter cells contain the same information for properties for heredity as the mothercell: mother cell and daughter cell are genetically identical. Mitosis is the type of division that gives rise to daughter cells for the purpose of tissue growth, regeneration or asexual (vegetative) reproduction. Definition, function and timing of the mitosis


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
